Integrative Lifestyle Medicine
INTUITION & INTELLECT
Harvest Your Hard Work
This is the season for restoring balance, tending digestion and immunity, and supporting mood and metabolism before the darker months ahead. Discover how personalized, natural medicine can help you harvest vitality now and carry it through the winter.
Meet the Team
-

Dr. Emily Anne McDonald, MD
LIFESTYLE MEDICINE, DipIBLM
Passionate about integrative and environmental approaches to women’s health, preventing disease, and improving the affordability and accessibility of holistic medicine with a strong focus on lifestyle-based care.
-
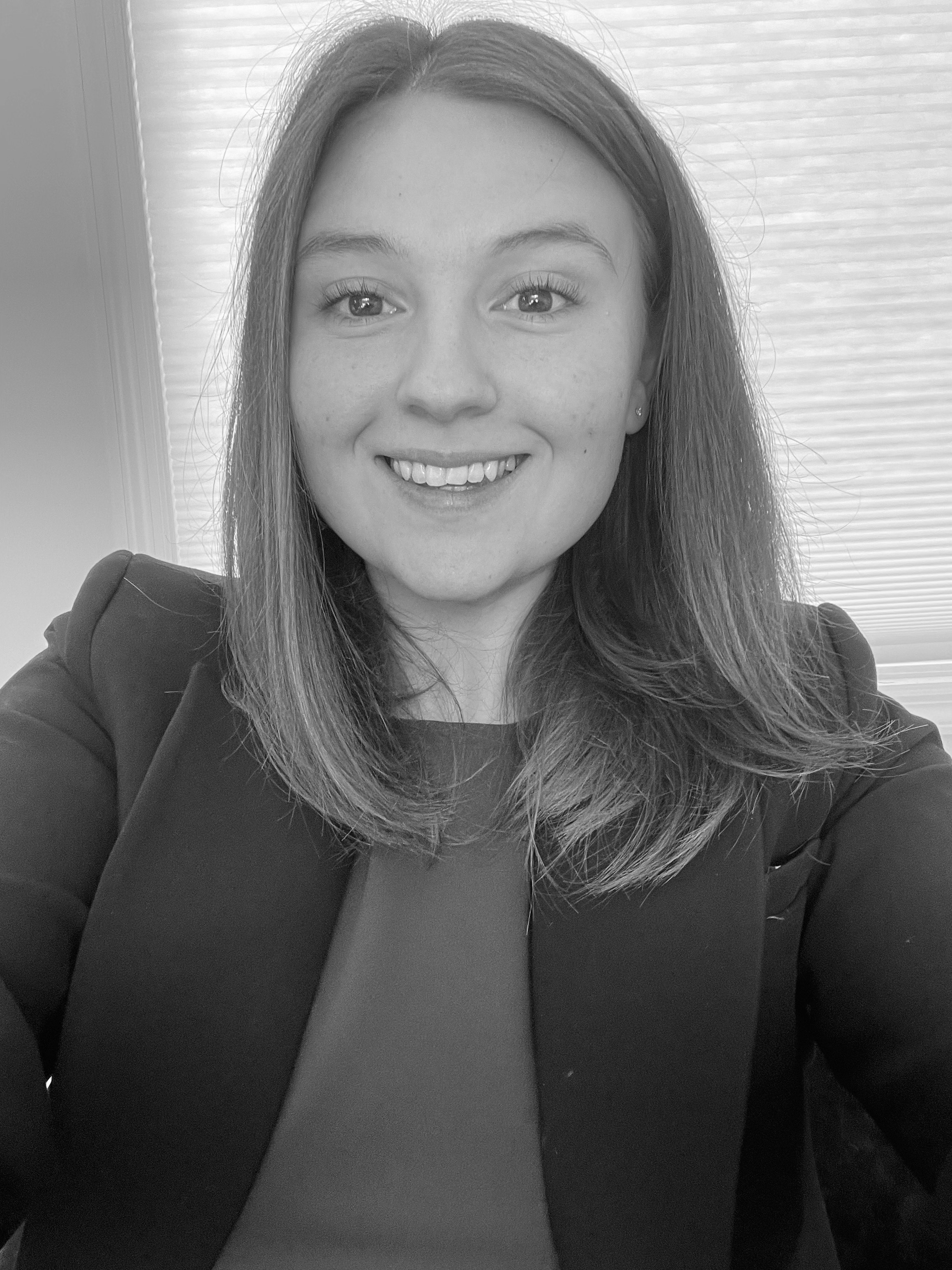

Kaitlyn McDougal, BS
CLINC CARE COORDINATOR
An advocate for functional holistic medicine, she integrates this approach into both her professional and personal life.
Design Lifelong Health
-

Gather Information
Thorough assessment of all medical information including labs, imaging, pathology, and more
-
Analyze Data
Identify trends and patterns in the medical data and correlate with subjective feelings and intuitive impressions
-

Implement Changes
Choose areas of focus to make changes or observe more carefully between sessions
-

Reflect on Process
Refine the health vision and values into focus and tailor a strategy to meet goals and needs
Upcoming Webinars and Events

Looking for More? Ask our Team.
We value making empowered decisions about health. Our insightful team of practitioners is here to listen and help you find answers that truly make a difference. Let’s get started!


